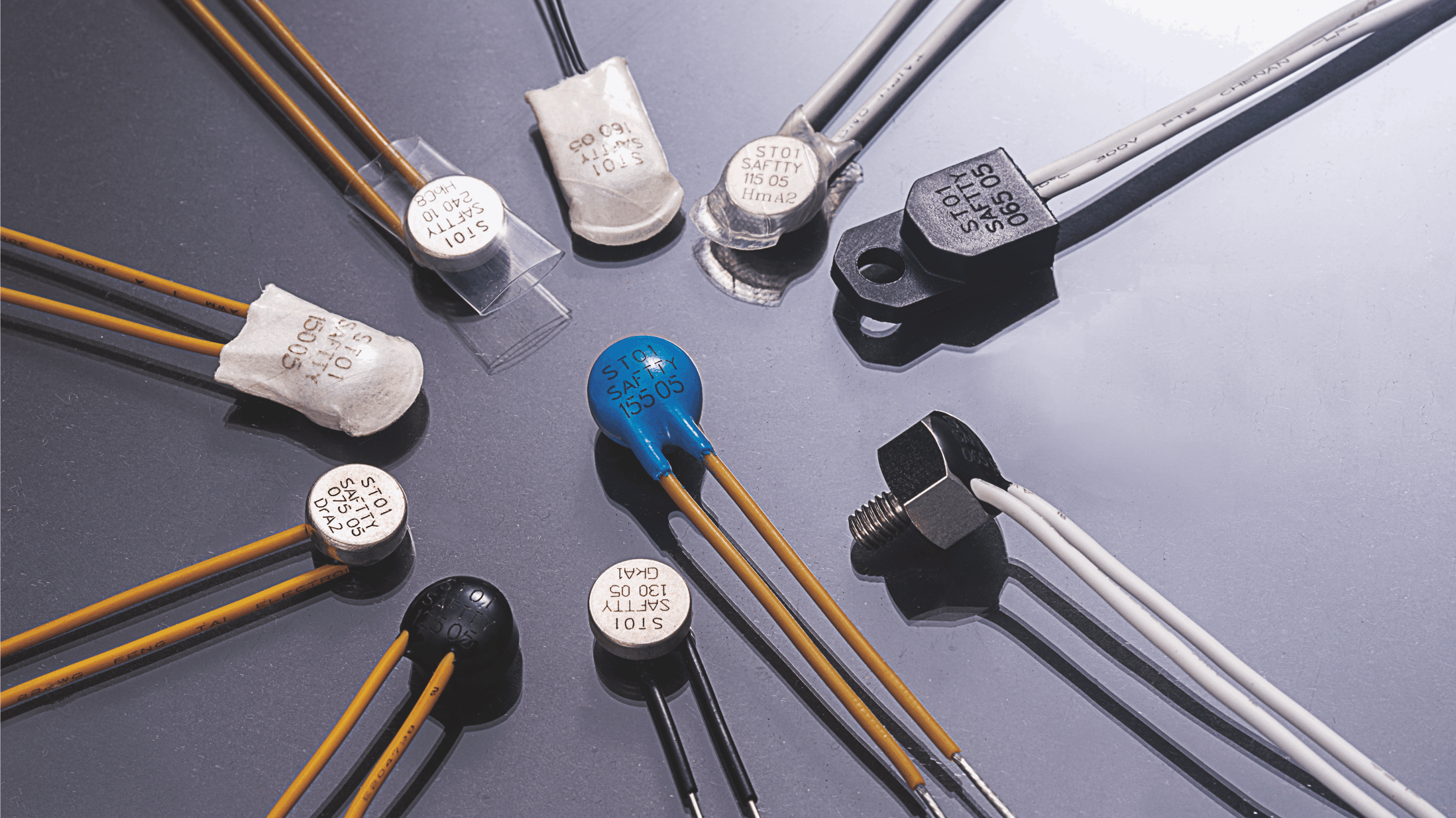
Electric motors and electrical equipment are the backbone of countless applications in manufacturing, automotive, HVAC, and household appliances. However, these systems are vulnerable to overheating due to overcurrent or prolonged operation. To prevent damage, thermal overload switches are employed as a critical safety mechanism.
Definition: What is a Thermal Overload Switch?
A thermal overload switch is a protective device that interrupts the flow of electrical current when it detects excessive heat caused by overcurrent or prolonged electrical loading. It acts as a fail-safe switch, preventing overheating that can lead to insulation failure, equipment burnout, or even fire hazards.
In simpler terms, it “senses” when a device or motor is getting too hot due to overload and automatically shuts it off to prevent damage.
How Does a Thermal Overload Switch Work?
Thermal overload switches typically use bimetallic strips or temperature-sensitive materials to detect heat. The switch operates based on the principle of thermal expansion:
Normal Operation: During normal conditions, current flows through the thermal overload switch uninterrupted.
Overload Condition: If the current exceeds safe limits, the electrical load causes the bimetallic strip to heat up.
Activation: The heat causes the bimetallic strip to bend or deform, opening the circuit and cutting off the current flow.
Cooling & Reset: Once the equipment cools down, the bimetal returns to its original shape, either automatically resetting or requiring manual reset, depending on the switch type.
Key Components of a Thermal Overload Switch
Bimetallic Element: The core sensing element made of two metals with different expansion rates.
Contacts: Open or close the electrical circuit depending on the temperature condition.
Reset Mechanism: Determines whether the switch automatically resets or requires manual intervention.
Housing: Often heat-resistant and insulated for safe installation within or near electrical equipment.
Common Applications
Thermal overload switches are widely used in both consumer and industrial devices:
Electric Motors: To prevent winding damage due to overheating.
Pumps and Compressors: Protect against overload during prolonged operation.
HVAC Systems: Safeguard components like fans, blowers, and compressors.
Power Tools: Prevent burnout when tools are used under excessive load.
Household Appliances: In washing machines, refrigerators, air conditioners, and more.
Transformers: Prevent overheating due to electrical faults or continuous heavy loading.
Types of Thermal Overload Switches
1. Automatic Reset
Automatically restores power once the temperature drops back to a safe level.
Suitable for applications where temporary overloads are normal.
Not recommended where unexpected restarts can be dangerous.
2. Manual Reset
Requires a human operator to manually reset the switch after a trip.
Ensures equipment is inspected before restarting.
Preferred in safety-critical systems such as industrial motors or compressors.
3. Integrated Thermal Overload Relays
Often used in motor starters.
Combines thermal overload protection with control features.
Works based on both current and time delay to prevent false tripping.
Benefits of Using Thermal Overload Switches
1. Enhanced Safety
The switch helps prevent motor burnout, short circuits, and potential fire hazards by cutting off power during high-temperature conditions.
2. Extended Equipment Life
By preventing overheating, thermal overload switches help extend the lifespan of motors, transformers, and appliances.
3. Reduced Maintenance Costs
Early interruption reduces the risk of costly damage, saving money on repairs and replacements.
4. Energy Efficiency
When a system runs under optimal conditions, it consumes less energy. Overload switches help maintain that balance.
5. Compact and Cost-Effective
Most thermal switches are small, easy to install, and relatively inexpensive compared to the cost of motor repair or replacement.
Thermal Overload Switch vs. Circuit Breaker
While both devices offer overload protection, they serve slightly different purposes:
Feature | Thermal Overload Switch | Circuit Breaker |
Detects | Heat due to overload | Current surge or short circuit |
Reset Type | Manual or automatic | Manual |
Response Time | Slower (for long-term overload) | Faster (instant for fault) |
Application | Motors, transformers | Entire circuits, panels |
Cost | Lower | Moderate to high |
For best protection, thermal overload switches are often used alongside circuit breakers in motor control systems.
Selection Tips for Thermal Overload Switches
When choosing a thermal overload switch, consider the following factors:
Rated Current and Voltage: Match the switch to the equipment’s electrical ratings.
Trip Temperature: Select a trip point appropriate for your application.
Reset Type: Choose between automatic and manual reset based on safety requirements.
Environment: Consider dust, humidity, and temperature when selecting the housing.
Standards Compliance: Look for UL, IEC, or CE certifications.
A thermal overload switch is a crucial component in modern electrical systems, designed to safeguard motors and other devices from overheating and damage. Whether in heavy industrial machines or everyday household appliances, these switches play a vital role in enhancing safety, reliability, and performance.
Understanding how they work and choosing the right type for your application can prevent costly downtime and extend the lifespan of your equipment. As industries continue to automate and digitize, thermal protection solutions like overload switches are more important than ever for smart, safe operation.





 中文
中文 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 한국어
한국어 にほんご
にほんご


